这是一个增长的网络模型,类似于森林火灾通过点燃附近的树木蔓延的方式。
详细信息
森林火灾模型旨在重现以下在真实网络中观察到的网络特征
重尾入度分布。
重尾出度分布。
社区。
密度化幂律。网络随时间推移根据幂律规则密度化。
收缩直径。网络的直径随时间减小。
网络以以下方式生成。一次添加一个顶点。该顶点连接到(引用)网络中已存在的 ambs 个顶点,这些顶点是均匀随机选择的。现在,对于每个被引用的顶点 \(v\),我们执行以下过程
我们生成两个随机数,\(x\) 和 \(y\),它们是几何分布的,均值分别为 \(p/(1-p)\) 和 \(rp(1-rp)\)。 (\(p\) 是
fw.prob,\(r\) 是bw.factor。)新顶点引用 \(v\) 的 \(x\) 个传出邻居和 \(y\) 个传入邻居,从那些尚未被新顶点引用的邻居中选择。如果可用的此类顶点少于 \(x\) 或 \(y\) 个,那么我们会引用所有这些顶点。相同的过程适用于所有新引用的顶点。
注意
已发表论文中的模型版本是不正确的,因为它无法生成作者声称的那种图。一个更正后的版本可从 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~jure/pubs/powergrowth-tkdd.pdf 获得,我们的实现基于此。
参考文献
Jure Leskovec, Jon Kleinberg 和 Christos Faloutsos. Graphs over time: densification laws, shrinking diameters and possible explanations. KDD '05: Proceeding of the eleventh ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery in data mining, 177–187, 2005.
参见
sample_pa() 用于基本优先连接模型。
随机图模型(游戏)bipartite_gnm(), erdos.renyi.game(), sample_(), sample_bipartite(), sample_chung_lu(), sample_correlated_gnp(), sample_correlated_gnp_pair(), sample_degseq(), sample_dot_product(), sample_fitness(), sample_fitness_pl(), sample_gnm(), sample_gnp(), sample_grg(), sample_growing(), sample_hierarchical_sbm(), sample_islands(), sample_k_regular(), sample_last_cit(), sample_pa(), sample_pa_age(), sample_pref(), sample_sbm(), sample_smallworld(), sample_traits_callaway(), sample_tree()
作者
Gabor Csardi csardi.gabor@gmail.com
示例
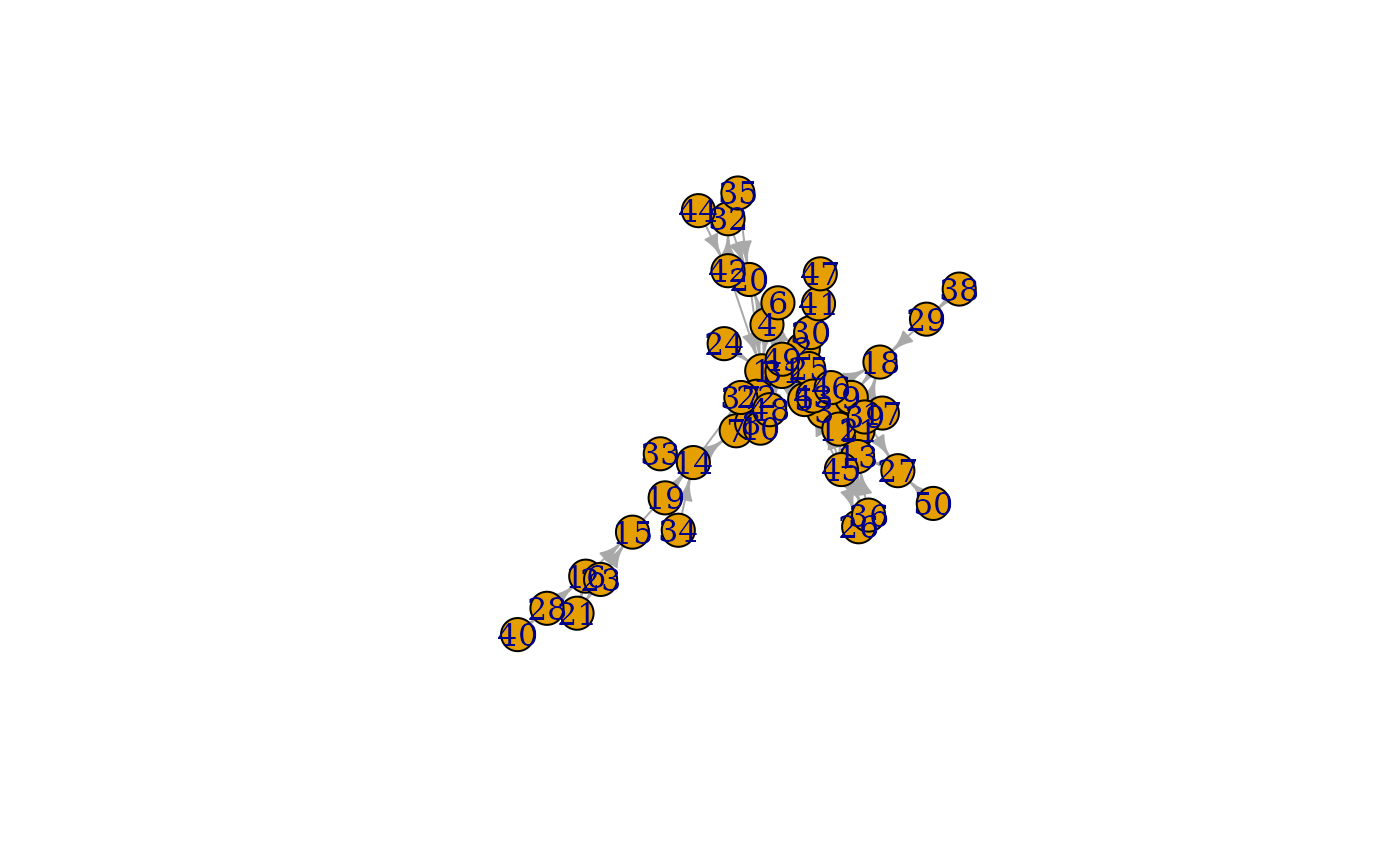
fire <- sample_forestfire(50, fw.prob = 0.37, bw.factor = 0.32 / 0.37)
plot(fire)
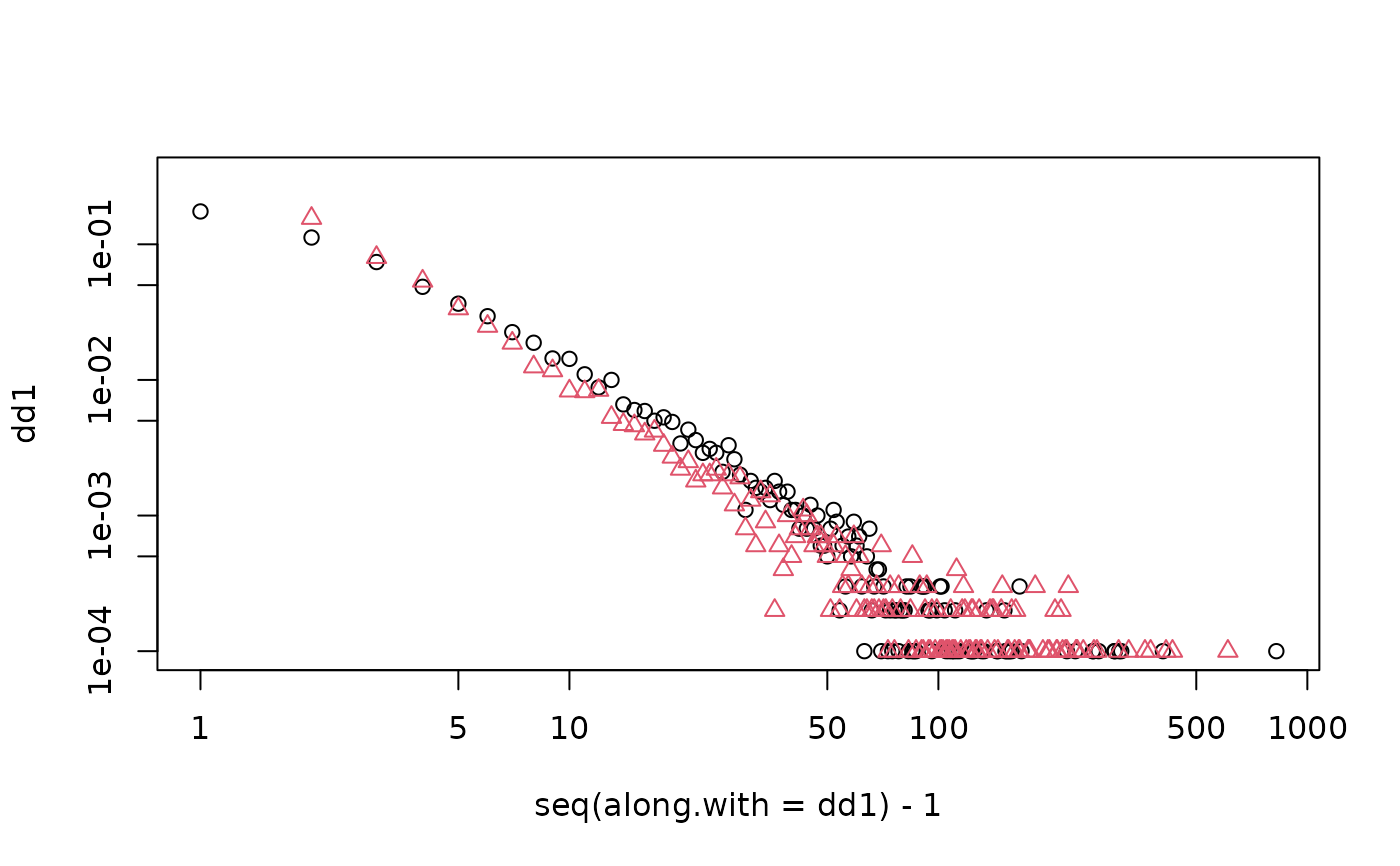
 g <- sample_forestfire(10000, fw.prob = 0.37, bw.factor = 0.32 / 0.37)
dd1 <- degree_distribution(g, mode = "in")
dd2 <- degree_distribution(g, mode = "out")
# The forest fire model produces graphs with a heavy tail degree distribution.
# Note that some in- or out-degrees are zero which will be excluded from the logarithmic plot.
plot(seq(along.with = dd1) - 1, dd1, log = "xy")
#> Warning: 1 x value <= 0 omitted from logarithmic plot
#> Warning: 692 y values <= 0 omitted from logarithmic plot
points(seq(along.with = dd2) - 1, dd2, col = 2, pch = 2)
g <- sample_forestfire(10000, fw.prob = 0.37, bw.factor = 0.32 / 0.37)
dd1 <- degree_distribution(g, mode = "in")
dd2 <- degree_distribution(g, mode = "out")
# The forest fire model produces graphs with a heavy tail degree distribution.
# Note that some in- or out-degrees are zero which will be excluded from the logarithmic plot.
plot(seq(along.with = dd1) - 1, dd1, log = "xy")
#> Warning: 1 x value <= 0 omitted from logarithmic plot
#> Warning: 692 y values <= 0 omitted from logarithmic plot
points(seq(along.with = dd2) - 1, dd2, col = 2, pch = 2)